Math 10 Common
Unit 1: Measurement
General Outcome 1: Develop spatial sense and proportional reasoning.
In this unit, you will solve problems involving ...
- Linear measurement
- Conversions within or between SI and imperial systems
- Surface area and volume of three-dimensional (3-D) objects
- Right triangles and trigonometry
Chapter 3 Right Triangle Trigonometry
Big Ideas
When you have completed this chapter, you will be able to...- Apply the Pythagorean theorem and primary trigonometric ratios to solve problems involving right triangles
- Solve problems involving indirect and direct measurement
- Solve right triangles
Specific Outcome: It is expected that students will:
4. Develop and apply the primary trigonometric ratios (sine, cosine, tangent) to solve problems that involve right triangles.
[C, CN, PS, R, T, V]
General Notes
Prior knowledge from previous grade levels includes:
- the Pythagorean theorem (Grade 8)
- similar polygons (Grade 9).
- This outcome is the students’ introduction to trigonometry; the primary trigonometric ratios are no longer developed in Grade 9.
The relationship between corresponding angles formed by two parallel lines and a transversal is not covered in previous grades. As a result, teachers may need to explain the relationship between an angle of elevation and the corresponding angle of depression.
In problems that involve multiple steps, rounding in calculations is to be done only after the last step.
Achievement Indicators |
Acceptable Standard |
Standard of Excellence |
| 1.4.1 Explain the relationships between similar right triangles and the definitions of the primary trigonometric ratios. | Provide a partial explanation of the relationships | Provide a complete and detailed explanation of the relationships. |
| 1.4.2 Identify the hypotenuse of a right triangle and the opposite and adjacent sides for a given acute angle in a triangle | ** | |
| 1.4.3 Solve right triangles | ** | |
| 1.4.4 Solve a problem that involves one or more right triangles by applying the primary trigonometric ratios or the Pythagorean theorem. | Provide a full solution for problems involving one right triangle or a partial solution for problems involving more than one right triangle | Provide a full solution for problems involving more than one right triangle. |
| 1.4.5 Solve a problem that involves indirect and direct measurement, using the trigonometric ratios, the Pythagorean theorem and measurement instruments such as a clinometer or meter stick | Provide a partial explanation of the solution. | Provide a detailed explanation of the solution. |
3.1 The Tangent Ratio
Focus on...
- Explaining the relationships between similar triangles and the definition of the tangent ratio
- Identifying the hypotenuse, opposite side, and adjacent side for a given acute angle in a right triangle
- Developing strategies for solving right triangles
- Solving problems using the tangent ratio
Hypotenuse
The side opposite the right angle in a right triangle
Always the longest side but less than the sum of the other two
Theta θ
Greek letter used to indicate an unknown angle
Opposite side
Side across from the acute angle being considered in a right triangle.
Adjacent side
the side that form one of the arms of the acute angle being considered in a right triangle, but is not the hypotenuse.
Tangent ratio
For an acute angle in a right triangle, the ratio of the length of the opposite side to the length of the adjacent side.
tan θ = opposite side / adjacent side
θ = tan-1( opposite side / adjacent side )opposite side = adjacent side * tan θ
adjacent side = opposite side / tan θ
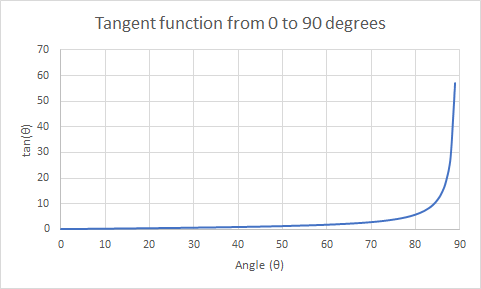
See a graph of the tangent function and a table of values
3.2 The Sine and Cosine Ratios
Focus on...
- Using the sine ratio and cosine ratio to solve problems involving right triangles
- Solving problems that involve direct and indirect measurement
Sine ratio
For an acute angle in a right triangle, the ratio of the length of the opposite side to the length of the hypotenuse
sin θ = opposite side / hypotenuse side
θ = sin-1( opposite side / hypotenuse side )opposite side = hypotenuese side * sin θ
hypotenuse side = opposite side / sin θ
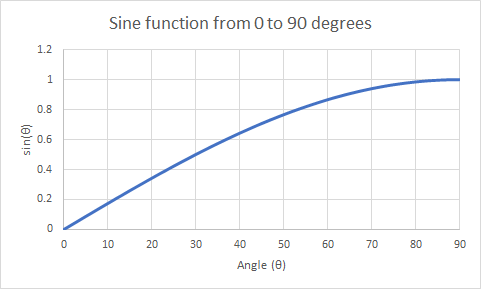
See a graph of the sime function and a table of values
Cosine ratio
For an acute angle in a right triangle, the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse
cos θ = adjacent side / hypotenuse side
θ = cos-1( adjacent side / hypotenuse side )adjacent side = hypotenuese side * cos θ
hypotenuse side = adjacent side / cos θ
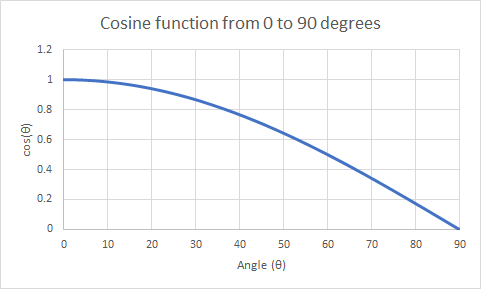
See a graph of the cosine function and a table of values
3.3 Solving Right Triangles
Focus on...
- Explaining the relationships between similar right triangles and the definitions of the trigonometric ratios
- Solving right triangles, with or without technology
- Solving problems involving one or more right triangles
angle of elevation
An angle of elevation is the angle between the line of sight and the horizontal when an observer looks upward.
angle of depression
An angle of depression is the angle between the line of sight and the horizontal when the observer looks downward.